Western African inhabitants
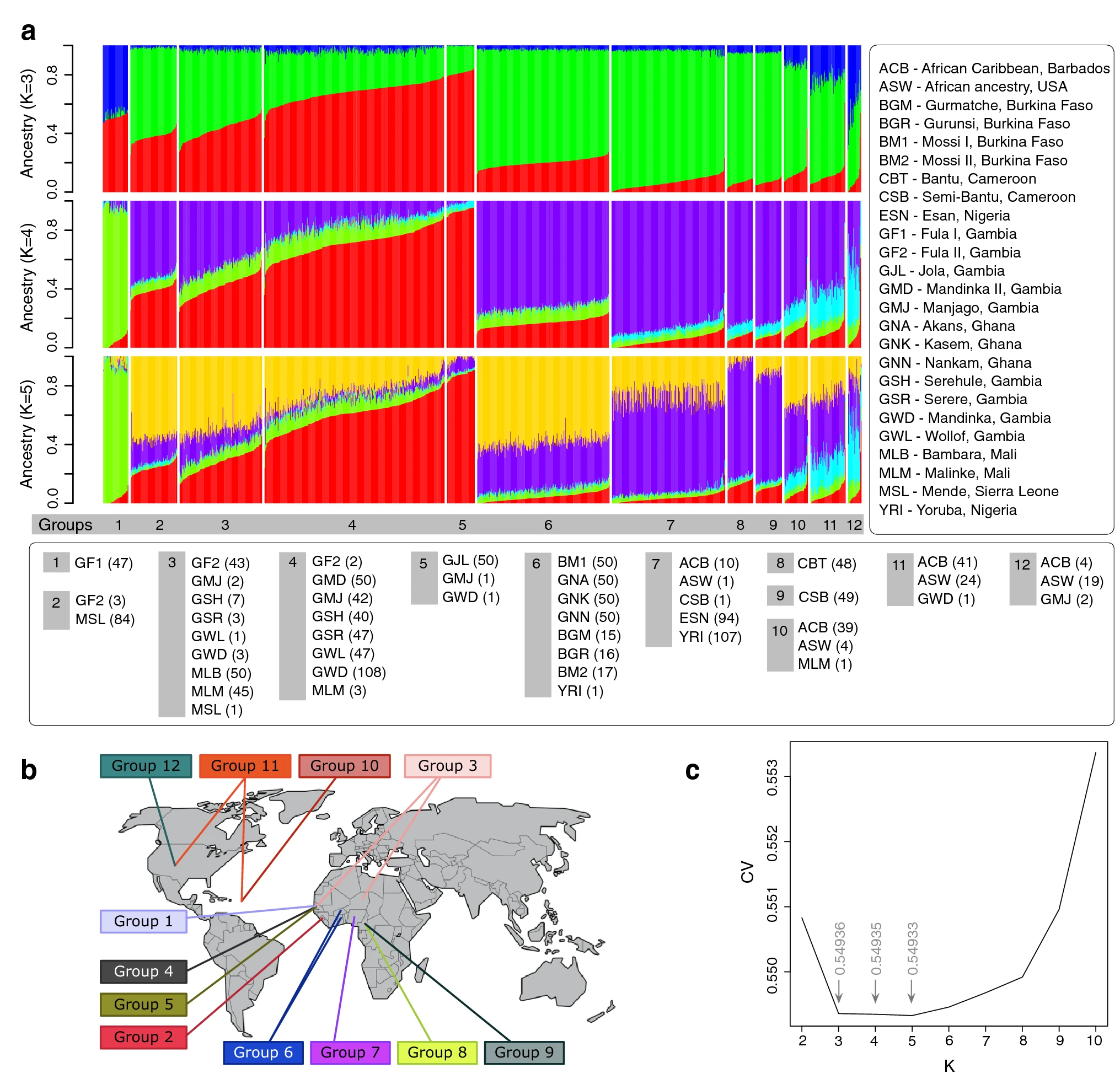
The investigation of population structure permits 1) relegating people to distinct ethnic gatherings living together at a specific locale, 2) examining movements from the cause of admixed populaces, and 3) evaluating and portraying bewildering of shared hereditary parentage in affiliation contemplates. Movement from one population into another locale will prompt admixture between the tribal gatherings leading to another admixed relative populace. African inhabitants are the most seasoned population in advancing current human species, given its single source in the African mainland between 200,000 years back and 350,000 years earlier, proofed by archeologists. African dialects have been ordered into different fundamental semantic families. Plant-growth-specialist populaces widely speak Niger-Kordofanian across Africa’s wide geographic conveyance. These heaps of conditions, atmospheres, diet, ways of life, and irresistible infection openness add to reliable particular pressing factors upon the African inhabitants, whose genome-wide genetic profiles have huge potential in uncovering principle parts of human population history and inherited vulnerability to sicknesses. The investigation of African and African American inherited diversity was overviewed with 1,327 microsatellites from the expansive mainland population categorized by self-depicted ethnic and phonetic gatherings. This homogeneity was checked in the Western African inhabitants of the Sahel Belt when utilizing ADMIXTURE. These inhabitants presented changing extents of just two bunches. One was more successive in Atlantic Western inhabitants (e.g., 90% in Mandenka). The other one was more continuous in Western/Central inhabitants, particularly in Esan and Yoruba of Nigeria (arriving at 74–81% recurrence). The Bantu relocation further greatly upset the first African family southerly of its place of source and somewhat influenced the more southern Sahelian populaces.
Known population analysis tools, fineSTRUCTURE and CHROMOPAINTER, have been applied to the African setting and tackled Western African bunching to a fine-scale size. The evidence indicated that most of sub-Saharan inhabitants shared a specific degree of inheritance from outside their present geographic area (dividing among various linguistic gatherings, for instance, western Bantu speakers having some contribution from western Pygmies). Further analysis, IPCAPS have been applied to Western African samples to build up a proof-of-idea for the analytic tool for fine-scale population structure. IPCAPS revealed that Western African inhabitants were in line with ADMIXTURE and fineSTRUCTURE results. Fine-scale population structure has been found in the Western African inhabitants utilizing IPCAPS as a hereditary grouping tool. The quantity of IPCAPS-assigned groups was generously more modest than the genuine number of African ethnic gatherings taken as info. Some IPCAPS-assigned groups were comprised of mixed African subpopulations. Nonetheless, three important fine-scale population structures were featured in the African inhabitants living in Cameroon, Gambia, Mali, Southwest USA, and Barbados.
Read the technical details at DOI: 10.1007/s00439-019-02069-7
 Preview figure from the article
Preview figure from the article